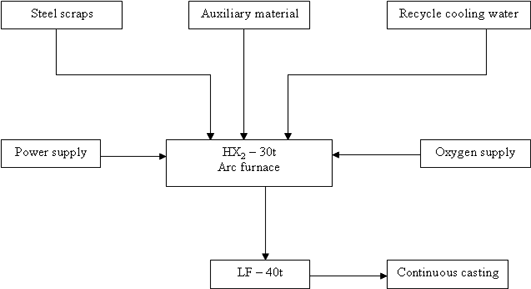
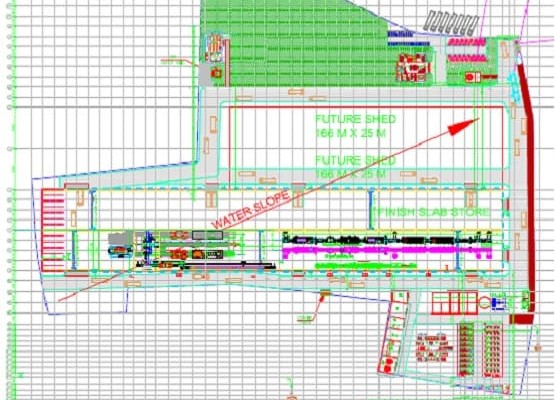
The industrial plant should be designed only after a complete production plan, plant layout and equipment sequences are determined so that the building exactly fits the production needs of the plant. It is necessary to keep in mind all factors that may affect the functioning of the plant in the building.

Some of the important factors in planning company buildings are as follows:-
1. Nature of Manufacturing Process
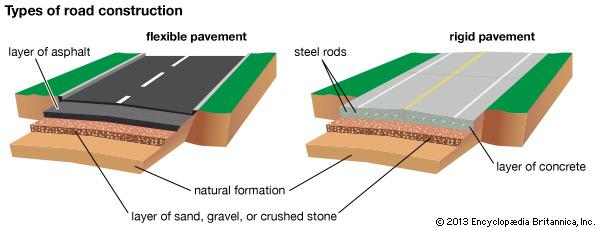
The type of construction process is the main determinant of plant buildings. The flat load, headspace, bay size etc., depended on the type of instruments or machines and equipment to be used.
2. Plant Layout
The form of instruments, help centers, and office practice significant control on the design and construction development of plant buildings. In case, labor pattern should be defined first and the building should be only a shell nearby this design. However, preparation for versatility should be made to meet the ultimate requirements.However, provision for flexibility should be made to meet the future needs.
3. Space Requirements
The area of factory buildings depends upon space requirements for the current flow and accommodation of materials, for the location of tools or machines, for service centers and for movement of employees. The height of the dome or ceiling depends upon the type of machine used. Use of overhead conveyors and tall accessories or equipment may need high roofs. But specific structures and additional costs may be involved. Pits may be dug, if possible, to provide all equipment.
4. Material Handling
Simplify in stock handling assists in the conversion of manufacturing cycle time avoids production bottlenecks and decreases material handling cost. Conveyor belts hoists, Cranes, etc., are frequently used for simple handling of materials. A modification in the number of columns and the maintenance of the ceiling at a desirable height are important to the use of material handling equipment. It is obvious that the requirements of efficient material handling equipment affect the building design. Conversely, the components of the factory building affect a firm’s ability to use this machine efficiently.
5. Plant Protection
The building should be so designed that there is sufficient stability of plant from an explosion, fraud, etc. Sprinkler system policy, fire rescue exits, automated alarms, outside hydrant, protection lights etc., may be used for this purpose.
6. Lighting
Brightness and Illumination system at intervals the plant uses a very important management on employees’ productivity and exhaustion. Therefore, lighting standards ought to be unbroken insight whereas plant coming up with.
7. Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning
It is completely common for large plants to provide separate constructions for providing high-forceful boilers. Their area will depend on melting conditions for production. Proper air-conditioning is necessary to provide sufficient fresh air. Some production processes need significant ventilation or managed temperature and moisture. Air conditioning is expressly common in the factory and other offices. Developing costs of power or energy have driven to new trends in warming, lighting and air conditioning. The rightful requirements of the Factories Act should also be met.

8. Service Facilities
Dexterities recounting to cooling towers, emergency power, compressed air, sewage treatment, etc., should also be considered in plant building. Waste control should be such that regulations regarding air and water decomposition, etc., are not disrupted.
9. Accessibility
The factory building should be designed to ensure free movement of workers in the plant.
10. Aesthetic Considerations
Forces should be made to establish the building a comfortable place to work for the employees. Their encouragement should receive top preference as they consume a lot of their entire working hours in the industry. The structure should have an elegant impression as this adds to the pride and influence of the employees and the management. Any charming, well-designed plant promotes area goodwill. It also has an impact on employees’ confidence. Such a plant proposes the progressive outlook of the organization. It is heartening to note that some management has spent special consideration to this factor at present demand.
11. Appearance
The developmental style and construction materials should be designed to give an engaging surface to plant buildings. A pleasant appearance, good garden setting, and clean surroundings are important to the local district.
12. Future Expansion
Ultimate development needs should be examined in planning a factory structure. If multi-storied structures are to be expanded with additional stages, it must be planned in advance so that the primary structure has the adequate footing to bear the additional pressure.
13. Fire Protection
Necessity and concern for a fire security system should be taken into account while planning for a factory building. This has become necessary at today. Fire security systems differ from the traditional fire extinguishers to automated heat indicators and fire security devices in industries.
14. Environmental Protection
Need to protect the environment has to be considered while planning a plant layout. This is being vigorously advocated all over the world now. It has become statutory in India too. This involves assuring greenbelt all around the industry, floriculture and profluent disposal and water/air handling plant and wastage control systems, etc.
15. Effluent disposal
Wheresoever chemical processes are used in electroplating, tanneries, etc., profluent treatment of the emancipated water has become necessary. Hence a company building has to be designed for a profluent distribution system.
16. Air supply
While creating a plan for a factory building, needed care has to be taken for satisfactory Air supply. This can be achieved through sufficient air compressors.
17. Contractors, consultants, and collaborators
It is pleasing that the construction work is trusted to well-known consultants, undergone in constructing industrial buildings. The plan of the factory and its layout also depends on the direction of contributors — Indian and foreign when projects are produced as per professional collaboration between such parties.
18. Cost-economics
This is an essential aspect of a building. Excellent management preparation and efficient monitoring by use of modern managerial aids like PERT/Milestones can take down the cost of production considerably. Usually, the cost of production goes up due to delay in accomplishment, changes in the design, delay of work during construction, deletions of the initial design.
A different source of lavish investment is due to poor planning and acquisition of elements, use of inferior rank materials and lack of effective guidance. So a factory building plan has to take into account of all expense factors.














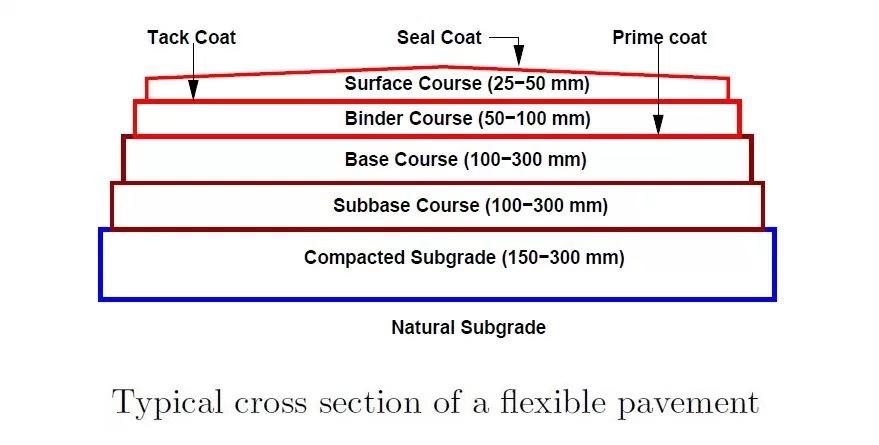
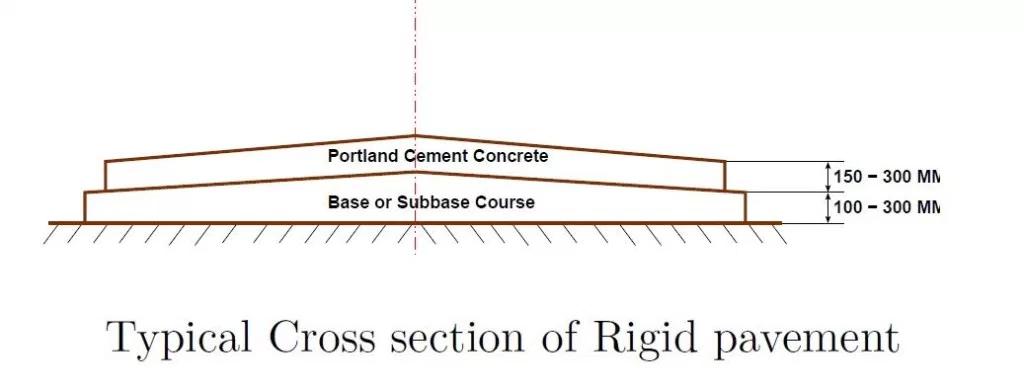

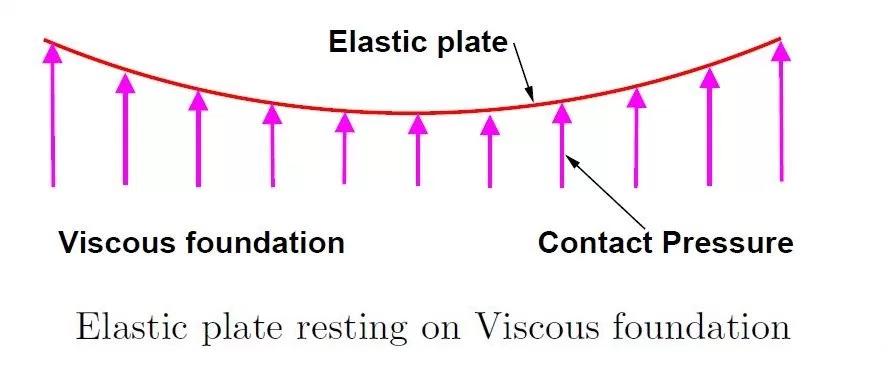









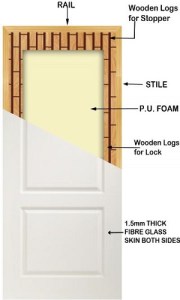


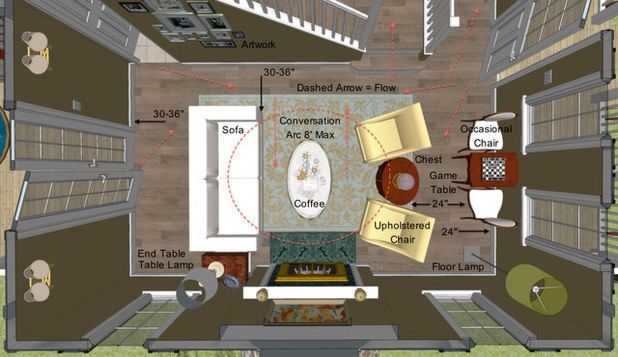
 1.A Single Couch
1.A Single Couch