There are huge types of doors and windows which can either be made or are accessible in the market ready to be fixed. Depending on the material of manufacture, some of their sorts alongside their main features, merits and demerits are offered here to encourage simple determination for the house proprietor.
1 Timber Wood

Customarily, timber or wood as it is prevalently known has been the mainstay for the manufacture of doors/windows. Its main advantage being its local availability of material and the simplicity with which it can be made by the local craftsmen.
Without further ado wide range of wood are accessible in the market and its choice ought to be made in light of the properties of life span and the financial plan of the owner. In spite of the fact that they can be utilized for all areas as a part of the house, they are best put for exterior areas.Timber is most normally being utilized for making of doors/windows.
2 Battened & Ledged Doors

Battened and ledged doors are the easiest type of doors and are being used for ages. Such doors comprise of vertical wooden battens of the stature of the door with around 35 mm thicknesses which are typically tongue and groove joint. Generally, three edges (level individuals) are given, one each at the top and base and one in the center.
Battened and ledged entryways can likewise be either braced or braced and framed to offer strongness and better appearance.Such doors are ordinarily used for toilets, showers, WC and furthermore in houses where the economy is of prime thought.
3 Framed & Paneled Doors

These kind of doors and windows are most usually used in the houses. The frame for the door is made of wood and the shutter panels with timber, plywood, piece board, hardboard. Various design plans can be made on the boards, in this manner making such door entirely brightening.
The panels can similarly be made out of glass. In situations where part of the door is in wooden panels and the remaining is of glass panels, the door is known as paneled and glazed. Such entryways have a flexible design which can look tastefully satisfying. The plan can be made as per the requirement and area in the house. The door frame for such sorts of doors can be made out of wood itself or of metal segments like steel.
4 Flush Doors

A flush door is a totally smooth door, having plywood or Medium Density Fiberboard over timber frame which is relatively light. The hollow core so acquired is frequently filled with a cardboard core material.
Flush doors are most regularly used in the inside of an abode, despite the fact that with a few varieties they are also utilized as exterior doors in houses.The frames for such doors can be made of wood, steel and so on, which can hold its weight. The doors are generally pivoted along one side to permit the way to open in a single way.Flush doors are generally given in houses nowadays because of the reasons of budget, appearance, solidness and so forth, and are usually accessible in the market.While giving these ways to toilets, showers; the internal face of the door ought to be secured with aluminum sheets to give insurance against water.Frames for such doors/windows can be made in any of the conventional ways.
5 Glass Doors

A glass is generally used for doors and windows, for the most in paneling. In any case, if the owner so wants, doors can be made out of glass for particular locations. Regularly such doors are given on the backside of the house as it gives an unobstructed view of the lawn or garden.
Front doors made of glass are similarly lovely, yet care ought to be taken to guarantee both protection and strength. Cut glass panels set into wooden edges are an incessant and wonderful alternative for front doors. Such doors are expensive and require great support.They are normally heavier than other doors other than being expensive.
6 Steel Doors

Steel or other such metal construction has been utilized for quite a long time as they are productive and are a durable choice for interior and exterior doors alike. These entryways can be either be hollow or solid.
It has been observed to be a decent substitute for wood and is being utilized widely to make frames. The frames can be made out of points, Tee, channels or pressed steel plates. Holdfasts and hinges are typically welded to the frame if there should arise an occurrence of steel frames.
Normal shutters made out of wood can be fixed on these steel frames.Steel frames are entirely prevalent and are being utilized widely for houses and different areas as they are sparing than the customary wooden frames.Shutters can likewise be made out of Mild Steel (MS) sheets, welded or bolted to a frame of angle iron or channel segment, appropriately supported.Steel doors can likewise be made of high caliber in cold rolled mild steel, precision engineered. They are durable requiring minimum maintenance. They are accessible in wonderful shades with different wood grain finishing.These can constantly be utilized where security is of a more noteworthy concern.
7 PVC Doors

PVC is a typical term for Poly Vinyl Chloride. It is essentially a plastic material generally utilized for making different items including water tanks, funnels, and fittings for houses. The utilization of PVC for the manufacturing of doors has turned out to be exceptionally famous and a vast assortment of the same are accessible in the market in various designs and colors.
The merits of utilizing PVC doors are that they are termite confirmation, solid, hostile to destructive, lightweight, dampness safe and so forth. They are likewise simple to manufacture and install.In any case, they are not suited for entry doors as they are light in weight, not weatherproof like wooden or metal doors, so they can’t avoid the cruel environmental conditions.Such doors available and can turn out to be more economical when contrasted and wooden doors.
8 Fiberglass Doors

Fiberglass is a glass which is drawn into fibrous frame and woven into fabric. It is solid, light and non-combustible and has a high rigidity. Glass strands bonded with resin that can be utilized to wide range of items including bathtubs, door and windows and so on.
Fiberglass is considered to stand out amongst the most hardened materials with generally low maintenance costs as related to wood and steel.Fiberglass doors are relied upon to be steady as they don’t twist, bow or contort. They are froth filled and offer great insulation properties.They can likewise be painted according to design.Doors and windows made out of fiberglass can be given wooden panels at first glance to enhance the feel. Entryways made out of fiberglass can be utilized for both outside and inside areas. The outside entryways have originator alternatives, for example, angled glass and entryway stiles.These doors are accessible in the market to coordinate any design style.
9 Fiber Reinforced Plastic Doors
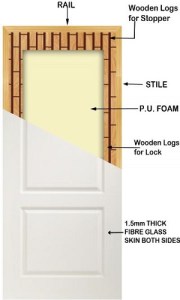
Fiber Reinforced Plastics famously known as FRP is a general term relating with the fortification of plastic with fibrous glass. Because of its high quality it can be put to numerous utilizations including manufacturing of doors. Normally, the elasticity is around ten times that of PVC. FRP formed doors are accessible in numerous colors and finishes incorporating normal wood finish in the market. The standard door thicknesses are 30/35 mm and are accessible with fire retardant properties.
These doors can likewise have two leaves of 1.5 mm thickness. The leaves are shaped over a core material framing a sandwich board.Essential wooden supports are accommodated for fixing the handles, locks, stoppers and other accessories. FRP doors are in huge demand nowadays for use in modern houses.
10 Aluminium Doors

Aluminum is a metal which has been put to huge number of applications due to being light in weight. An extensive number of items made out of aluminum are accessible in the market including doors, windows, partitions and much more.
Aluminum frames for doors and windows have the advantage of resisting tough weather conditions. Being light in weight they exchange less loads to the base. Aluminum frames are not influenced by termites and all things considered they are longer enduring.Doors and windows made out of aluminum can be side hung or sliding and are reasonable for outside or inside areas.Stylishly they are very satisfying and are entirely practical over the long haul.


 1.A Single Couch
1.A Single Couch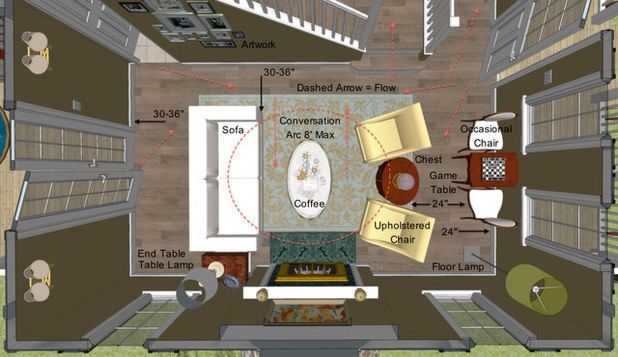















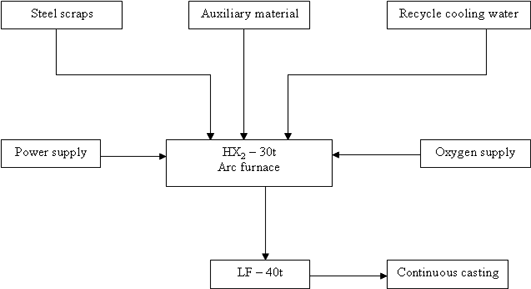
























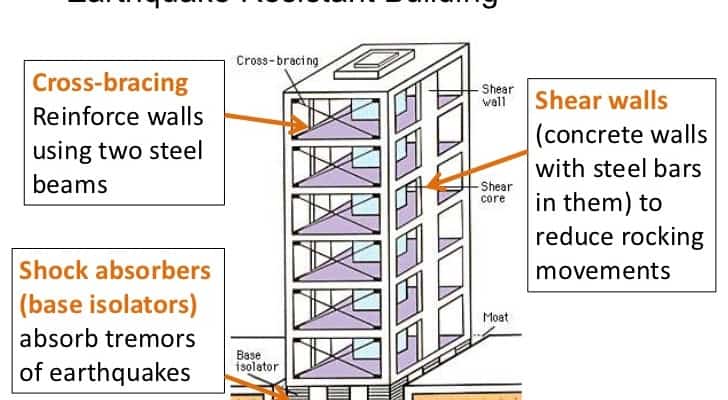
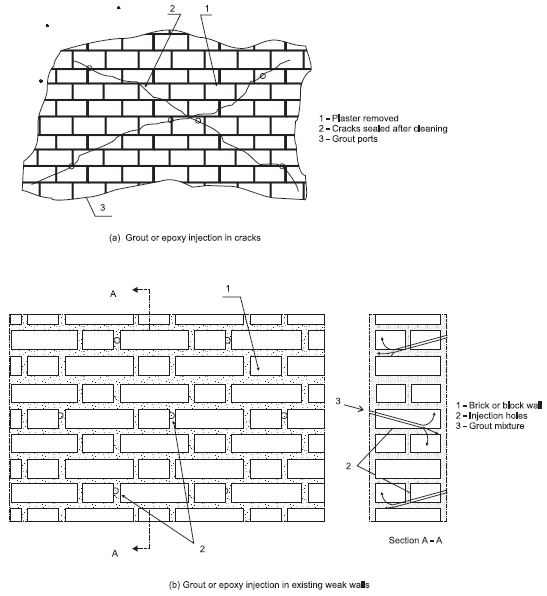
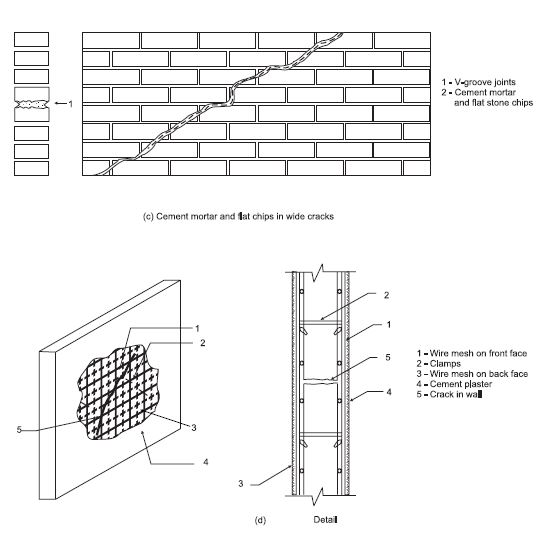
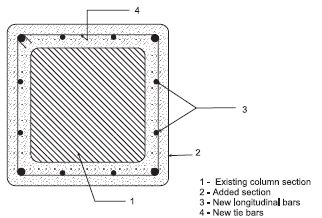 Â